
 The lead battery is manufactured by using lead alloy ingots and lead oxide It comprises two chemically dissimilar leads based plates immersed in sulphuric acid solution. The positive plate is made up of lead dioxide PbO2 and the negative plate with pure lead. The nominal electric potential between these two plates is 2 volts when these plates are immersed in dilute sulfuric acid. This potential is universal for all lead acid batteries. Therefore, a 12 volt lead acid battery is made up of six cells that are connected in series are enclosed in a durable plastic casing.
The lead battery is manufactured by using lead alloy ingots and lead oxide It comprises two chemically dissimilar leads based plates immersed in sulphuric acid solution. The positive plate is made up of lead dioxide PbO2 and the negative plate with pure lead. The nominal electric potential between these two plates is 2 volts when these plates are immersed in dilute sulfuric acid. This potential is universal for all lead acid batteries. Therefore, a 12 volt lead acid battery is made up of six cells that are connected in series are enclosed in a durable plastic casing.
The capacity of the battery depends on the amount of lead dioxide on the positive plate; sulfuric acid present in the battery; and, the amount of spongy lead on the negative plate. During discharging process, the suphate ions in the electrolyte interact with the positive and negative plates and form lead sulfate on them. This result in the reduction of specific gravity of the electrolyte in proportion to the charge delivered to the load.
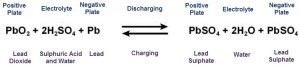
During the charging process, the cycle is reversed, that is, lead sulphate and water are converted to lead, lead oxide and electrolyte of sulphuric acid by an external charging source. This process is reversible, which means lead acid battery can be discharged or recharged many times. The chemical formulas of charging and discharging process of the lead acid batteries is given above.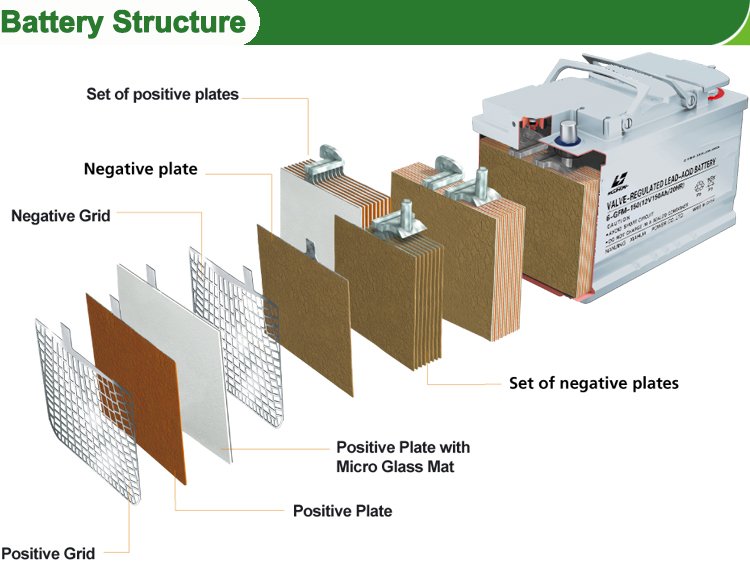
The main parts of the battery are plates, i.e., anode and cathode plates, separators, electrolyte or sulphuric acid, case, cell connectors and terminals, as shown in the above figure.
Batteries are manufactured using careful maintenance of equipments in an automated controlled environment. The Manufacturing processes can be divided into several stages like Oxide and grid production process, pasting and curing, assembly process, formation, filling, charge-discharge process, final assembly, inspection and dispatch. These manufacturing steps are briefly explained below.
Lead oxide is obtained by masses of lead from melting furnaces either by Milling or Barton Pot process methods. In the milling process, the tumbling action generated by the rotating mill on solid lead generates heat and then the surface of the lead gets oxidized. The surface layers of the oxide are removed while the lead particles roll in the drum. In Barton Pot process a fine stream of lead droplets is produced by blowing air on molten lead. These droplets are reacted with oxygen and produce lead oxide.
Manufacturers consider the pasting material as a trade secret,and therefore not reveal this to public. However, this paste material in general is made with oxide of lead, red lead, litharge, water and dilutes sulphuric acid. These pastes are used to fill the grids, i.e., positive and negative grids; but, for both, the pastes are not exactly filled with the same material, some expander materials are added for making negative paste.
After the formation, batteries are subjected to high-rate discharge test for short duration to rule out any defects before sending them out to the final charge. After discharging and recharging batteries for several times to attain best working condition, these are inspected and tested with some measuring instruments.
This is all about the lead-acid battery manufacturing process carried out in several battery production industries. We hope that the given content might have been helpful for the readers. Furthermore, for any information like electronic circuits for charging batteries, battery capacity selection and battery safety methods you can contact us.